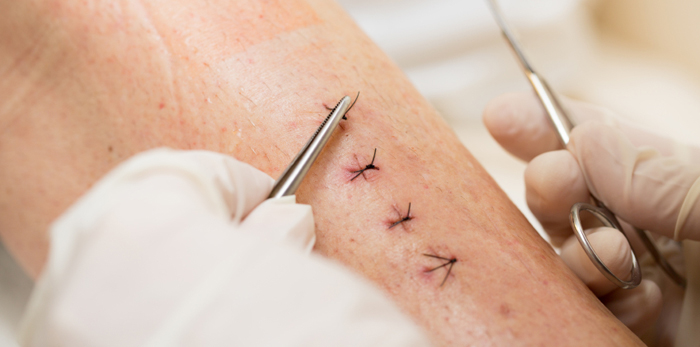
Sutures are sterile, surgical threads used to repair cuts and close incisions from surgery. Common called stitches; they are a helpful medical device used in holding together those skin and tissues of human body that are severed by surgery, incision or injury. They are strong and elastic enough to hold skin, internal organs, blood vessels and virtually any tissue of the human body. Sutures are helpful in wound closure and they support wound healing. Many kinds of sutures are available based on their properties and uses.
In broad terms, sutures can be classified into two groups –
- Absorbable sutures
- Non-absorbable sutures
The absorbable types are those that break down in tissue after a specific period of time. They are created in a manner to degrade within as a wound or incision heals. On the other hand, the non-absorbable types won’t dissolve in the body and only a surgeon can remove them upon healing of the incision.
More so, types of sutures will also depend on the characteristics and features needed for closure of wounds. They have to be strong so that they won’t break in the body easily; they have to be non-toxic to not cause any infection risk; and more importantly, they have to be hypoallergenic to not cause any adverse reaction in the body.
Similarly, sutures types will also depend on their flexibility level as this helps doctors tie and knot them in an easy manner. They also have to be created in a manner to stop fluids to enter the body from outside and cause infections.
1# Suture types based on material structure
Monofilament and multifilament are two sutures types when we classify them based on material structure. The multifilament ones are created to provide superior knot security while the monofilament types offer better passage through tissues. Out of the two, the monofilament types lead to lower tissue reaction while the other one is coated with various materials.
2# Suture types based on size
Suture classification is also done on the basis of their size. So, you can expect them to get in a number of sizes and meet varied purposes. In general, sutures with higher diameter will have superior tensile strength and support particular procedures perfectly. The diameter size for both collagen and synthetic sutures will range between 0.020 to 0.999 millimeters (mm).
3# Suture types based on raw material origin
Raw material origin is also a criteria upon which sutures are divided. As per this classification, we get natural and synthetic sutures. Barring silk and catgut sutures, all others are synthetic in nature.
4# Suture types based on coating
Sutures can also come with coatings on the surface and some of the materials used for the purpose include silicon, wax, chromium salt, calcium stearate and PTFE. Some sutures may also come with antibacterial or antimicrobial coating to gain superior healing qualities. Some may not have any type of coating at all.
5# Suture types based on uses
Based on their uses or application, sutures can be of different types, including –
- General sutures
- Veterinary sutures
- Cosmetic surgery sutures
- Ophthalmic sutures
- Dental sutures
- Cardiovascular sutures
- Valve sutures
- Orthopedic sutures
- Gynecology sutures
 Living With Healthy Hunger Health Blog
Living With Healthy Hunger Health Blog

