 Cardiologists play a crucial role in managing pediatric heart diseases. They focus on diagnosing, treating, and preventing heart problems in children. Their expertise ensures that young patients receive the care they need. Understanding conditions like congenital heart defects and rhythm disorders is vital. It’s not just about the heart, though. Cardiologists often work with other specialists to provide comprehensive care. For instance, managing issues like spider veins Manhattan requires collaboration for the best outcomes. This approach helps in delivering effective treatment and improving children’s overall health.
Cardiologists play a crucial role in managing pediatric heart diseases. They focus on diagnosing, treating, and preventing heart problems in children. Their expertise ensures that young patients receive the care they need. Understanding conditions like congenital heart defects and rhythm disorders is vital. It’s not just about the heart, though. Cardiologists often work with other specialists to provide comprehensive care. For instance, managing issues like spider veins Manhattan requires collaboration for the best outcomes. This approach helps in delivering effective treatment and improving children’s overall health.
Understanding Pediatric Heart Diseases
Pediatric heart diseases encompass a range of conditions that affect the heart of a child. These include congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, and acquired heart diseases. Congenital defects are present at birth and may involve structural issues. Arrhythmias are irregular heartbeats that can disrupt the normal flow of blood. Acquired heart diseases develop after birth due to infections or other medical conditions.
The Role of Pediatric Cardiologists
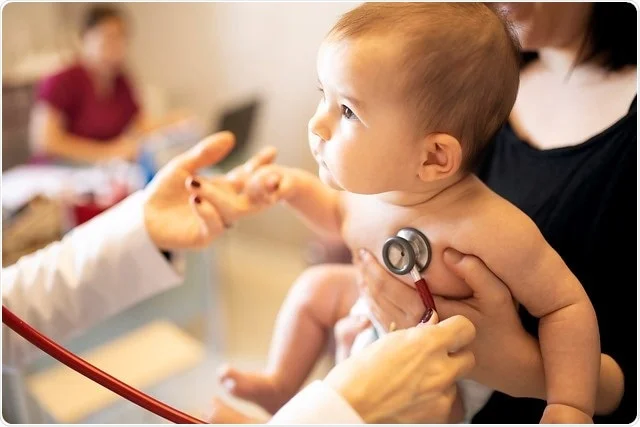
Pediatric cardiologists are specialists trained to handle these heart issues in children. They use a range of diagnostic tools to assess heart function. These tools include echocardiograms, electrocardiograms, and cardiac MRI. By understanding the unique aspects of a child’s heart, they can tailor treatment plans suited to individual needs.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
| Tool | Description |
| Echocardiogram | Uses sound waves to create images of the heart. |
| Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Measures electrical activity of the heart. |
| Cardiac MRI | Provides detailed images of heart structures. |
Treatment and Management
Treatment options vary based on the type and severity of the heart condition. Some children may need medication to manage symptoms, while others may require surgery to correct structural issues. In some cases, lifestyle changes are necessary to support heart health. Cardiologists work closely with families to educate them about these changes.
The Importance of Routine Care
Routine care is more effective after treatment. It’s crucial for monitoring heart health and preventing complications. Regular check-ups help track a child’s progress and adjust treatment as needed. This ongoing care ensures that any new issues are caught early.
Collaboration with Other Specialists
Pediatric cardiologists often collaborate with other healthcare providers. This team approach ensures comprehensive care for the child. Specialists such as pediatric surgeons, nutritionists, and physical therapists may be involved. For example, a child with a heart defect might need surgery, followed by dietary advice and physical therapy.
Research and Innovation
Research plays a significant role in advancing pediatric cardiology. Continuous study leads to improved treatments and outcomes. Innovations like minimally invasive surgery and better imaging techniques have transformed care. For more on current research, refer to trusted sources such as the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Concluding Thoughts
Managing pediatric heart diseases requires specialized skills and a compassionate approach. Cardiologists are key players in ensuring that children with heart conditions live healthy, fulfilling lives. By employing the latest diagnostic tools, collaborating with specialists, and focusing on ongoing care, they make a profound difference. For more insights, visit the Mayo Clinic for reliable information.
 Living With Healthy Hunger Health Blog
Living With Healthy Hunger Health Blog

